Nice Info About Why Are Curve Slopes Downward Origin Double Y Axis Column
It relates price changes to our satisfaction, real income, and choices.
Why are curve slopes downward. There are at least three accepted explanations of why demand curves slope downwards: The demand curve generally slopes down from left to right, due to the law of demand while the quantity demanded drops as the price rises for the majority of goods. The demand curve for an individual firm is downward sloping in monopolistic competition, in contrast to perfect competition where the firm's individual demand curve is perfectly elastic.
There are several causes for the downward slope of the demand curve. What is the economic reason that the aggregate supply curve, or short run aggregate supply curve, slopes up? ~ the aggregate supply curve slopes up because when the price level for outputs increases while the price level of inputs remains fixed, the opportunity for additional profits encourages more production.
This is due to the fact that demand increases when price falls and decreases when price rises. There are three essential theories why economists believe that there is a downward sloping aggregate demand curve. Demand curve slope downwards as because the individual buys more of a commodity at lower price.
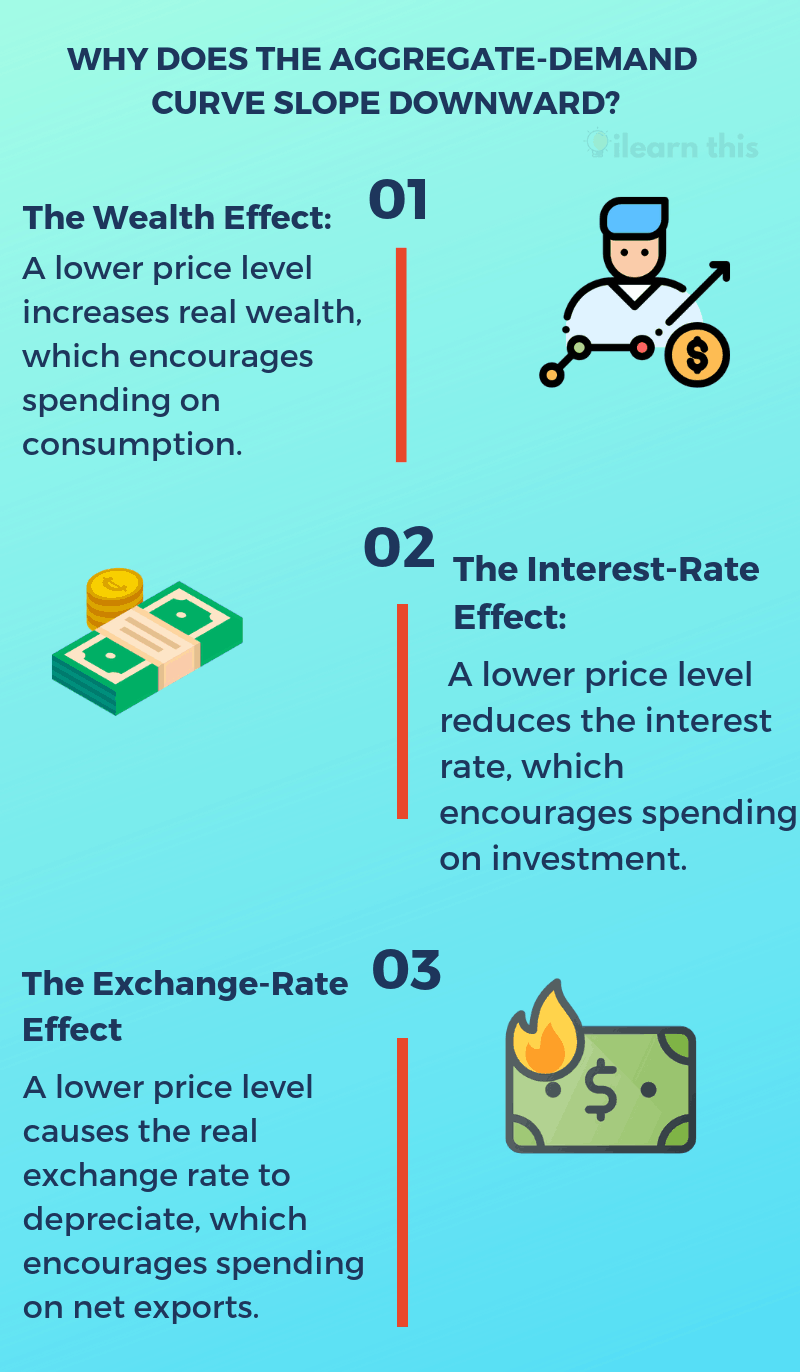
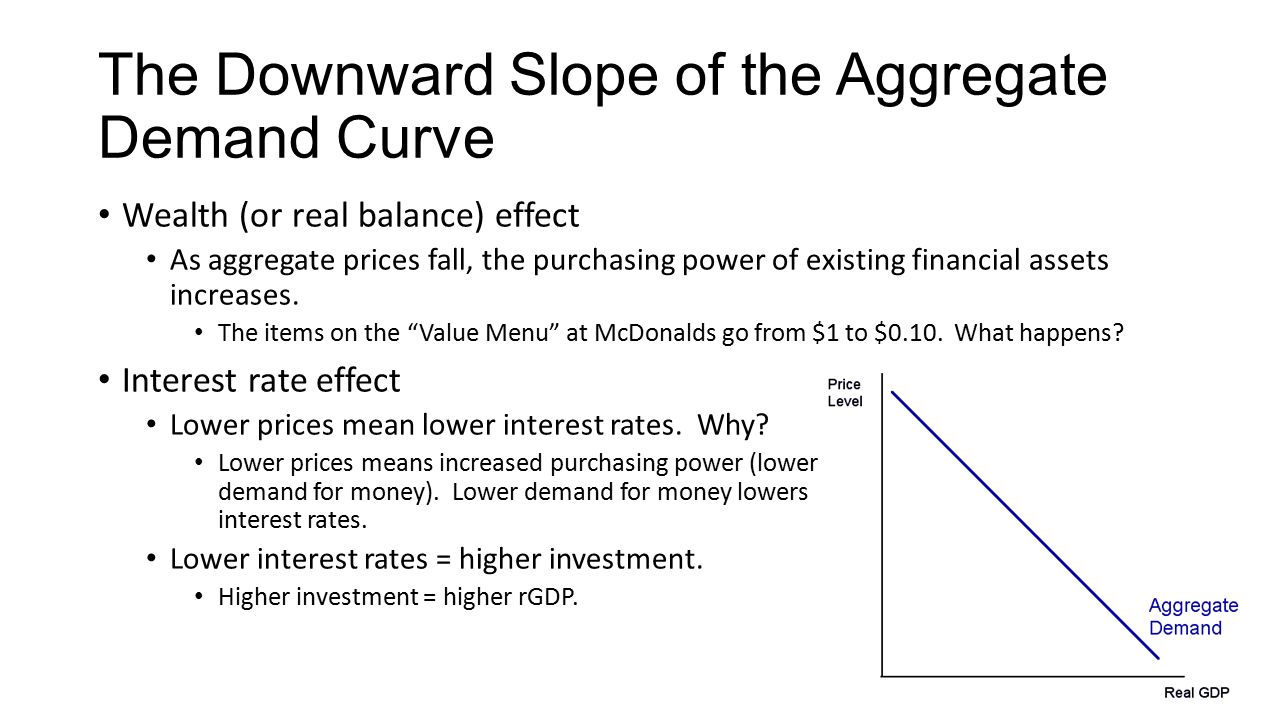
What are two reasons why the demand curve is downward sloping? 2) lower price, exports more competitive 3) lower interest rates Interest rate effect, wealth effect, exchange rate effect.
The production possibility curve is downward sloping from left to right because more of good x can be produced only with less production of good y, when the given resources are assumed to be fully and efficiently utilised, using the given technology. (image will be uploaded soon) higher price results in lower demand whereas low price results in higher demand. The horizontal shift is the change in autonomous demand times the multiplier 1 /(1 mpc ).
(1) the wealth effect, (2) the interest rate effect, and (3) the exchange rate effect. Generally, the demand curve slopes downward (i.e.its slope is negative) because the number of unit demands increases with a fall in price and vice versa. What are the 7 major causes of downward sloping demand.
The first is called the “wealth effect.” 1 the price level and consumption: The negative slope of a. A market demand curve, just like the individual demand curves, slopes downwards to the right, indicating an inverse relationship between the price and quantity demanded of a commodity.
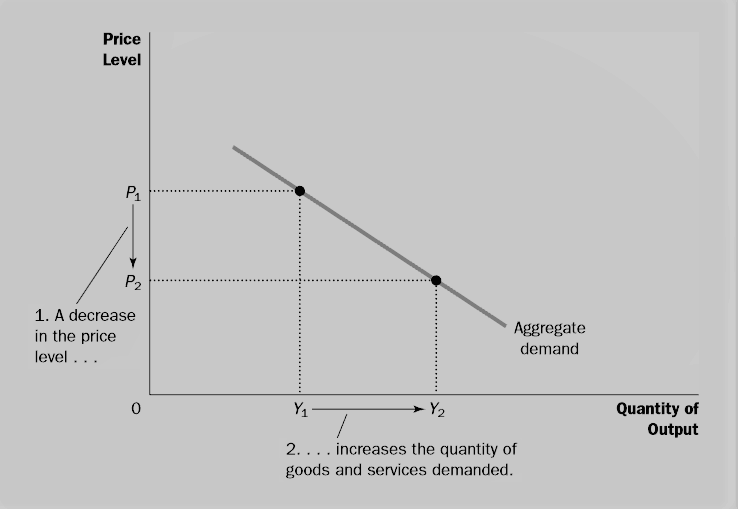
Demand curves generally have a negative gradient indicating the inverse relationship between quantity demanded and price. The following points highlight the seven main reasons for the downward sloping demand curve. By doing so, we can identify three distinct but related reasons why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping:
Explore three reasons for this: Though the price is the primary or direct reason for the rise and fall in demand, there are several other (indirect) reasons that result in the rise and fall in demand. The demand curve always slopes downwards from left to right.
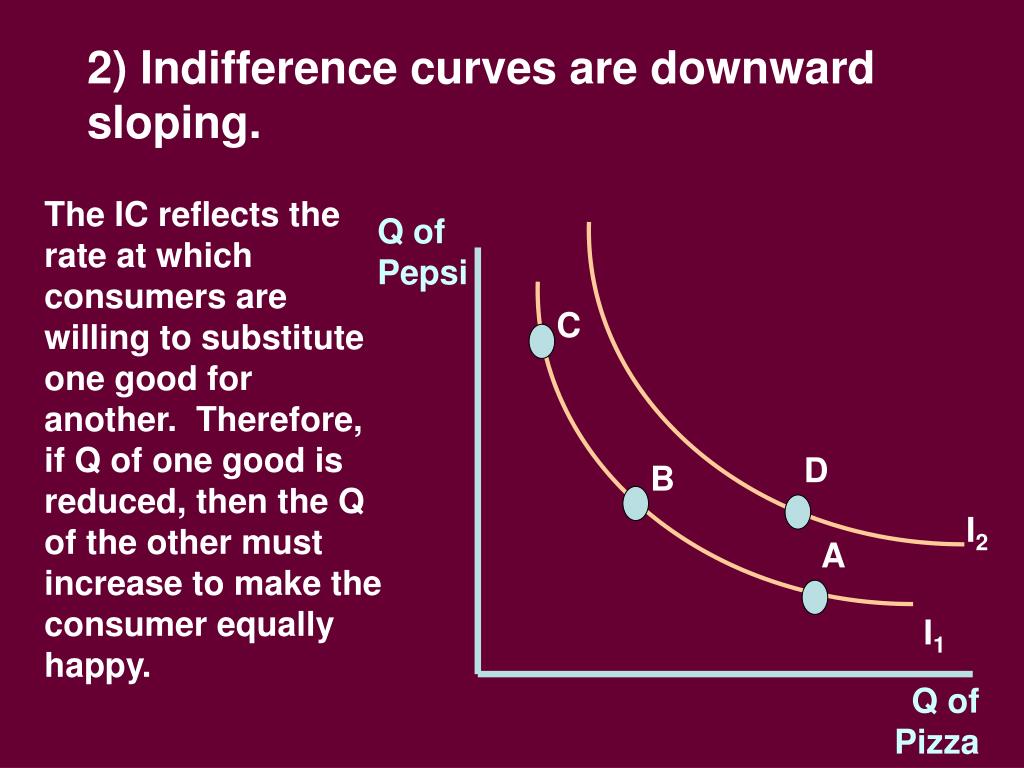
Diminishing marginal utility, the income effect, and the substitution effect. As the price increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and, conversely, as the price decreases, the quantity demanded increases. The demand curve is downward sloping because, as per the law of demand price change and quantity change are in the opposite direction.